Both sprocket types transfer energy created by the chainsaw’s powerhead via the clutch cover to rotate the chain around the guide bar. However, their methods are different enough to spark some heated debate.
The sprocket type that comes with a new chainsaw is most often chosen by the manufacturer or at best the tech who puts it together at the store. If you are lucky enough to have a local shop that will customize your new saw at the time of purchase, then you have a choice to make and you might lose a few friends in the process.
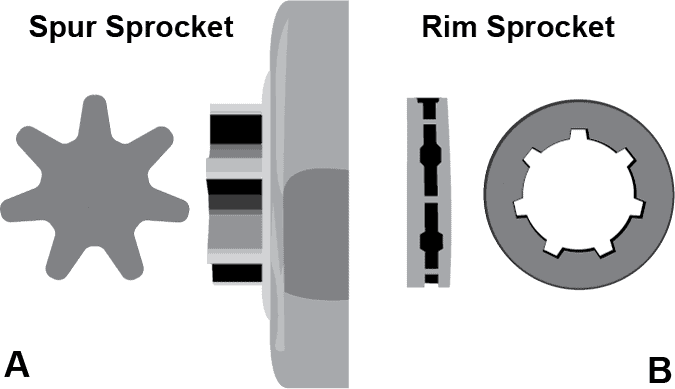
Figure A: Spur Sprocket, Figure B: Rim Sprocket
If your chainsaw model allows, choose a rim-style drive sprocket. Rim sprockets are better than spur sprockets because they are easy to maintain, offer increased flexibility and have a lower cost. Unless you have a very specific use case, you will be happier with a rim drive sprocket and so will your chainsaw.
Ok, those might be fighting words in some circles, but hear me out. When looked at holistically, rim drive sprockets offer several advantages over spur drive sprockets. In my opinion, spur sprockets only offer a slight increase in durability. Rim sprockets give you much more flexibility and convenience.
What is the difference between a spur and rim drive chainsaw sprocket?
Spur sprocket
A spur sprocket, also called a hub sprocket, is a multi-pronged star-shaped sprocket wheel (usually between 6 and 8 points) that is integrated into the chainsaw’s clutch cover to form a single monolithic part. Engine power is transferred directly from the clutch cover to the chain through this single rotating part.
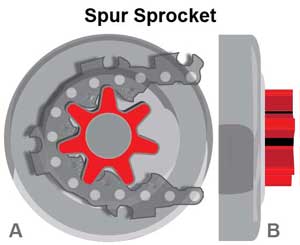
Rim Sprocket
A rim sprocket is a multi-pronged star-shaped gear (usually between 6 and 8 points) that is sandwiched between two discs to form a series of channels for the chain to ride in. The rim sprocket is free-floating, riding on the clutch cover’s splined hub. Engine power is transferred to the clutch cover’s hub, which rotates the rim sprocket and chain.
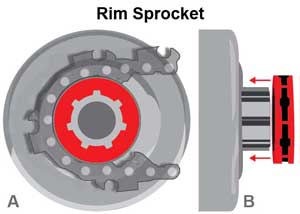
6 Benefits of using a rim sprocket on your chainsaw
- Easier to maintain and replace. Rim sprockets ride on a clutch cover with a splined hub. Held on with a washer and “E”clip, they can easily be replaced without the need to replace the clutch cover. This is great for repairs out in the woods.
- Better chain alignment. The rim sprocket is free floating on the clutch housing’s splined hub. This allows for better lateral alignment of the chain’s drivers with the guide bar groove, reducing bar wear and derailments.
- Quicker customizing. Regardless of the rim sprocket’s tooth count, pitch or guage, the interior dimension does not change. This makes it faster and easier to change a chainsaw’s performance or cutting components.
- Lower cost. Rim sprockets are less expensive to buy than spur sprockets.
- More convenient. Its small size and cost makes it an easy addition to any field kit. Having a replacement on hand will keep your chainsaw running even when you are miles away from town.
- Resilient. Less likely to be damaged when a chain derails. Usually the chain will slip to the side and not chew up the sprocket teeth.
- Adaptable. Rim sprockets can adjust to different guide bar thicknesses. Whereas a spur sprocket’s wear groove may not line up correctly when using a different guide bar. This is important when changing bar length for different cutting needs or wood species.
3 Benefits of using a spur/hub sprocket on your chainsaw
- Durability: Beefier construction and less contact areas with the chain drivers.
- Simpler: Fewer parts to break or loose. It’s just one monolithic part
- Easier chain installation: Does not require the user to back off the chain tension as much to remove and instal a chain.
Should I change my spur sprocket to a rim sprocket now?
A rim sprocket is a nice-to-have. There is no reason to replace a functioning spur sprocket until it has worn out. The spur sprocket that came with your saw will work reliably until it has worn out. At that time you should consider replacing it with a rim sprocket and consider replacing your bar as well.
When should you replace a drive sprocket?
Both rim and spur drive sprockets should be replaced after wearing out 2 chains or if it is damaged. If you use multiple chains per cutting session, replace the drive sprocket when you replace the guide bar. For a deeper dive, check out my article: When To Replace Your Chainsaw’s Drive Sprocket.
What about tooth count? Does it matter?
The number of teeth on your drive sprocket will directly affect the speed and cutting characteristics of your chainsaw. It is best to stick with the tooth count that came with your saw from the factory, but if you have specific cutting needs it can make a noticeable difference especially if you use a skip chain or need to use a longer bar. See the Sprocket Configuration by Chainsaw Size article for more information.
